I learned that Germany’s healthcare system is simpler and more supportive than I expected. At first, I was nervous. I didn’t know how to find a doctor who spoke English or how German insurance worked. With time,
In this post, I will share my personal experiences as an expat mom who used Germany’s healthcare system for both childbirth and emergency care for my baby later on. I will also explain the basics of health insurance (public vs private), how to book appointments, and what to expect when you visit doctors or hospitals here.
I hope you will feel more confident about navigating healthcare in Germany by the end of this article. Whether you are an international student, a professional who moved for work, or a spouse raising a family in Germany, these insights are for you.
1. Overview of the German Healthcare System
1.1 Universal Coverage
Germany has a universal healthcare system, which means everybody living here must have health insurance, including expats. As an expat, you cannot legally stay in Germany long-term without valid insurance. This rule may sound strict, but the result is that most people have some level of coverage. You do not have to worry about being turned away from hospitals if you have insurance.
1.2 Public vs. Private Health Insurance
There are two main kinds of health insurance:
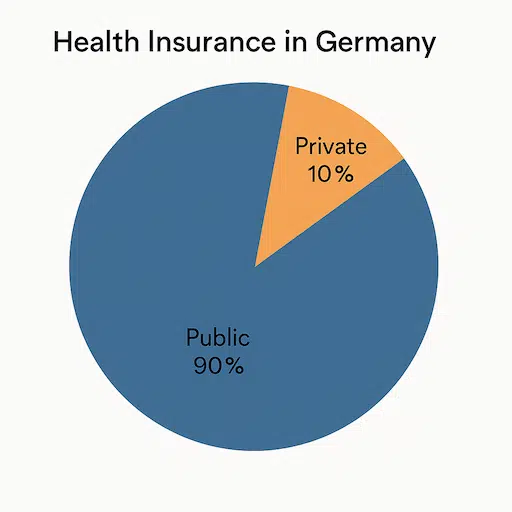
1. Public (Statutory) Insurance (GKV): Most residents (including many expats) use public insurance. If you have a normal job, the monthly cost is split between you and your employer, and it is based on your income. Public insurance covers most routine healthcare costs, hospital stays, and visits to the doctor. You usually pay very little out of pocket—often just small co-payments.
2. Private Insurance (PKV): Some people (like higher earners or self-employed expats) can choose private insurance. Private insurance often offers extra benefits (like single rooms in hospitals or shorter wait times), but the costs can change over time, sometimes rising as you get older. Also, switching back to public can be hard once you join a private plan.
In my case, I have public insurance. I found it simple and comforting to know that almost everything is covered. My spouse is also on public insurance, and our child is automatically covered under family insurance at no extra cost.
1.3 How to Access Healthcare
In Germany, you can choose your own family doctor (Hausarzt). You are not automatically assigned one, so you may have to call several clinics to find one that is accepting new patients. Many doctors speak at least basic English, especially in bigger cities. For specialists (like dermatologists or cardiologists), you usually need a referral from your family doctor, although this can vary. In emergencies, you can go directly to the hospital or call 112 for an ambulance.
I have prepared a PPT to give an understanding of the German Healthcare System
2. Childbirth in Germany: My Personal Experience
One of my biggest concerns when I first got pregnant in Germany was: How will I handle pregnancy and delivery in a foreign healthcare system? Looking back, it was smoother than I expected.
2.1 Pregnancy Check-Ups and Finding an OB/GYN
When I discovered I was pregnant, I asked friends for recommendations for an English-speaking OB/GYN (in German, Frauenarzt). I was lucky to find a clinic where most staff spoke English, especially Dr. med. Katja Lippmann. At my first visit, I received a special maternity booklet called a Mutterpass. This booklet tracks all my pregnancy health details, including weight, blood pressure, ultrasound results, and important medical history.
My public insurance covered regular check-ups, so I had no extra bills. The clinic staff explained everything step by step. Although my German was not perfect, they were patient and switched to English whenever I needed it.
2.2 Antenatal Classes (Elternschule)
In many parts of Germany, women have midwives (Hebammen) for pregnancy and postpartum care. However, in my situation, I could not find a midwife because they were all booked (this can happen if you do not contact a midwife early enough). Instead, we joined an Elternschule (parenting school) at the hospital. It was a series of classes about childbirth, caring for a newborn, breastfeeding tips, and handling the emotional side of becoming parents.

I was worried about the language barrier, but luckily, the teacher spoke enough English to help us understand the main points. We practiced relaxation and breathing exercises, and I also made new friends in a similar life stage. That support was wonderful for me as an expat. Public insurance often covers the cost of these antenatal classes, or you pay a small fee, depending on the course.
2.3 Delivery Day at the Hospital
When the big day arrived, I checked into the hospital that I had chosen and pre-registered at. One thing that surprised me about German hospitals is that you usually bring your own pajamas, slippers, toiletries, and sometimes baby clothes. The hospital provides the medical essentials, of course, but not always gowns or personal items. So, it felt like packing for a short trip!
During labor, the hospital staff was caring and attentive. I was nervous about pain management, but the midwives explained my options (such as an epidural). Communication sometimes happened in a mix of English and German, but overall, it worked fine. I stayed in a shared room with another new mother—this is standard for public insurance unless you pay extra for a private room. However, it did not bother me; in fact, I liked talking to someone else going through the same experience.
2.4 Postpartum Stay & Costs
After giving birth, I stayed in the hospital for two days because everything was normal. The nurses helped me learn baby-care basics (feeding, diaper changes, swaddling). They also gave me information about the U1 and U2 check-ups that happen soon after birth in Germany. The hospital handled my baby’s birth registration paperwork, which saved me a trip to the local registry office.
I was amazed that I did not receive a hefty bill when I was discharged. Public insurance covered almost everything. Some hospitals might charge a small daily fee (about €10 per day in some cases), but I only had to pay for minor extras like phone or TV access. If I compare it to what childbirth might cost in my home country, it was incredible.
3. Everyday Healthcare: What to Expect as an Expat
3.1 Finding a Family Doctor (Hausarzt)
If you plan to stay in Germany for a while, finding a family doctor immediately is wise, even if you do not feel sick. I called several nearby practices to check if they were taking new patients. Some said they were full, but others still had openings. Once I found one, I gave them my insurance card and signed a registration form. Now, I see this doctor for general check-ups and any minor illnesses.
If you want to use the online platform to find doctors. My suggested Applications are ClickDoc and Doctolib
3.2 Specialists and Wait Times
If you need a specialist (e.g., dermatologist, orthopedist), you often ask your family doctor for a referral. Germany can have long wait times for non-urgent specialist appointments—sometimes weeks or months. If you are privately insured, you may get faster appointments, but it varies. Urgent issues usually get faster treatment. For real emergencies, call 112 or go to the emergency room (Notaufnahme) at a hospital, regardless of your insurance.
3.3 Pharmacies (Apotheken)
In Germany, medicine is generally sold in pharmacies (Apotheken). Many over-the-counter drugs are kept behind the counter, so you must speak to the pharmacist. They will give you advice on how to use the medicine. Public insurance covers prescription medication, but you pay a small co-payment (usually around €5-10, depending on the drug). My experience has been that pharmacists are quite helpful, and you can always bring a translation app if you are unsure of certain words in German.
3.4 Surprising or Different Things
• Bring Your Own Supplies to Hospitals: If you stay overnight in a hospital, expect to bring your own comfortable clothes, shampoo, towels, and baby clothing if needed.
• Shared Rooms: Public insurance often means sharing a room with one or two other patients in the hospital.
• Less Paperwork for Patients: Usually, the clinic or hospital bills the insurance company directly. You rarely see large invoices yourself. I just show my insurance card at each visit.
• Preventive Check-ups: The system strongly encourages preventive care. Children have U-checks at different ages, and adults have some routine screenings covered by insurance.
4. My Child’s Hospital Stay: A Look at Emergency Care
About a year after my child was born, we faced a frightening situation. My little one developed a high fever and had a seizure at home. As an expat parent, I panicked, especially without family nearby. Here is what happened.
4.1 Calling for Help
I dialed 112 for an ambulance. They arrived quickly—within 10 minutes. I showed my insurance card and gave the basic information. Although my German was shaky under stress, the emergency responders were calm and professional. They will do their best to communicate if you do not speak German well. The main priority is helping the patient.
4.2 Admission to the Pediatric Ward
We ended up at the hospital’s pediatric ward (Kinderstation). The doctors ran tests to find out what caused the fever. My child was admitted for about seven days, during which I was able to stay in the room overnight. I learned that many German hospitals allow one parent to stay with a sick child, and this is covered by public insurance. That was a huge relief, as I did not want to leave my child alone.
4.3 Language and Staff Support
The nurses spoke some English, which helped me a lot. They made sure I understood the treatments (fluids, medication) and gave me updates on test results. I appreciated the patience and compassion shown to us. Even though I was worried and anxious, they tried to reassure me every step of the way.
4.4 Discharge and Costs
After a week, my child was well enough to go home. The entire hospital stay was billed directly to my public insurance. I believe I only got a small co-payment for the hospital stay (some insurance plans charge around €10 per day). That was it. No giant bill or complicated forms. Not having to worry about money was a major relief in that scary moment.
5. Public vs. Private Insurance: Choosing What Suits You
After experiencing childbirth and an emergency hospital stay, I can confirm that public insurance is very reliable. However, some expats do consider private insurance for various reasons:
1. Public (GKV)
• Pros: Comprehensive coverage, low out-of-pocket costs, and coverage of spouses and kids at no extra charge if they are not working. Accepted everywhere.
• Cons: Possible longer wait for some specialist appointments. High earners pay higher monthly premiums (since it is income-based). Shared hospital rooms if you need inpatient care.
2. Private (PKV)
• Pros: Potentially shorter wait times, private rooms, or more “luxury” services. For young or healthy individuals, premiums can be attractive initially.
• Cons: Premiums may rise over time, and switching back to public coverage may be difficult. You may have to pay costs upfront and get reimbursed. Family members often need separate policies.
Which is right for you? It depends on your income, age, health needs, and personal preferences. My advice: if you are coming with a family or plan to stay long-term, public insurance often feels simpler and safer. If you want certain perks or have a very high income, private might appeal to you—but do your research carefully.
6. Tips for a Better User Experience
6.1 Language and Communication
• If possible, find doctors or clinics that explicitly say they speak English (often listed on their websites).
• Bring a German-speaking friend or use a translation app when you must fill out forms or talk about complex health topics.
6.2 Plan for Specialist Visits
• Book routine check-ups well in advance. If you are in a large city, it can be tough to get an appointment on short notice.
• For urgent problems, call your family doctor’s office early in the morning—they usually reserve spots for same-day cases.
6.3 Keep Important Numbers Handy
- Emergency (ambulance, fire): 112
- Non-emergency medical on-call service (evenings/weekends): 116117
- Your insurance company’s hotline (they often offer English support).
6.4 Elternschule or Birth Preparation Courses
- If you cannot find a midwife (Hebamme), look for Elternschule classes at your hospital. They usually discuss breathing techniques and baby care and provide emotional support.
- Sign up early because these courses can fill up fast, too.
6.5 Paperwork and Registration
- Always carry your insurance card.
- If you have a baby in Germany, the hospital can often handle birth registration, which is very convenient.
- You usually fill out a simple form to add your newborn to your insurance. Ask your insurance provider for details.
7. Reflections: What I Learned and Why I Value German Healthcare
Living in Germany taught me that a universal healthcare system can bring peace of mind. When I look back on giving birth here and later seeing my child admitted to the hospital, I am thankful that costs were never the main worry. I could focus on recovery and caring for my family instead of battling bills or paperwork.
Of course, the system has small downsides—like waiting for non-urgent procedures or dealing with some forms in German. However, overall, the quality of care is high, and there are many safety nets for families. I was also touched by how much the medical staff tried to support us emotionally, not just medically.
8. Conclusion: Empowering Expats to Navigate With Confidence
If you are an expat planning to live in Germany, I hope my story helps you feel more prepared. Here are my final takeaways:
- Your first step is to sort out insurance. Public insurance is the easiest path for most. If you qualify for private insurance, do your research.
- Expect a primarily cashless system: Show your insurance card at each visit—most bills go straight to your insurer.
- Language worries are normal: Many professionals speak English but learn some German phrases for clarity, especially in emergencies.
- Be proactive: Book appointments early, find a good family doctor, and if pregnant, arrange care (midwife or Elternschule) as soon as possible.
- 5. Take advantage of the care: Germany’s focus on preventive check-ups and extended hospital stays for recovery might differ from your home country, but it is often beneficial.
Remember, your experience can vary by city or region, but the foundation remains the same: You will be covered and cared for. If you need more information, feel free to check official websites (like the Federal Ministry of Health) or reputable expat forums. Do not hesitate to ask in the comment section.
I hope you have a smooth journey navigating German healthcare. It might seem intimidating initially, but once you settle in, you might find, as I did, that it is a reassuring system, ready to help you and your family in sickness and in health.

