Germany’s roadways are known for their efficiency and organization; traffic signs play a significant role in maintaining this order. Whether you’re a tourist driving on the famous Autobahn or a local navigating city streets, understanding German traffic signs is essential for road safety and compliance with local laws.
We have prepared this self-study guide for beginners that will cover the types of traffic signs in Germany.
We found a very informative PDF that explains almost all Traffic signs. You can directly download it from here.
Download PDF of German Traffic Signs
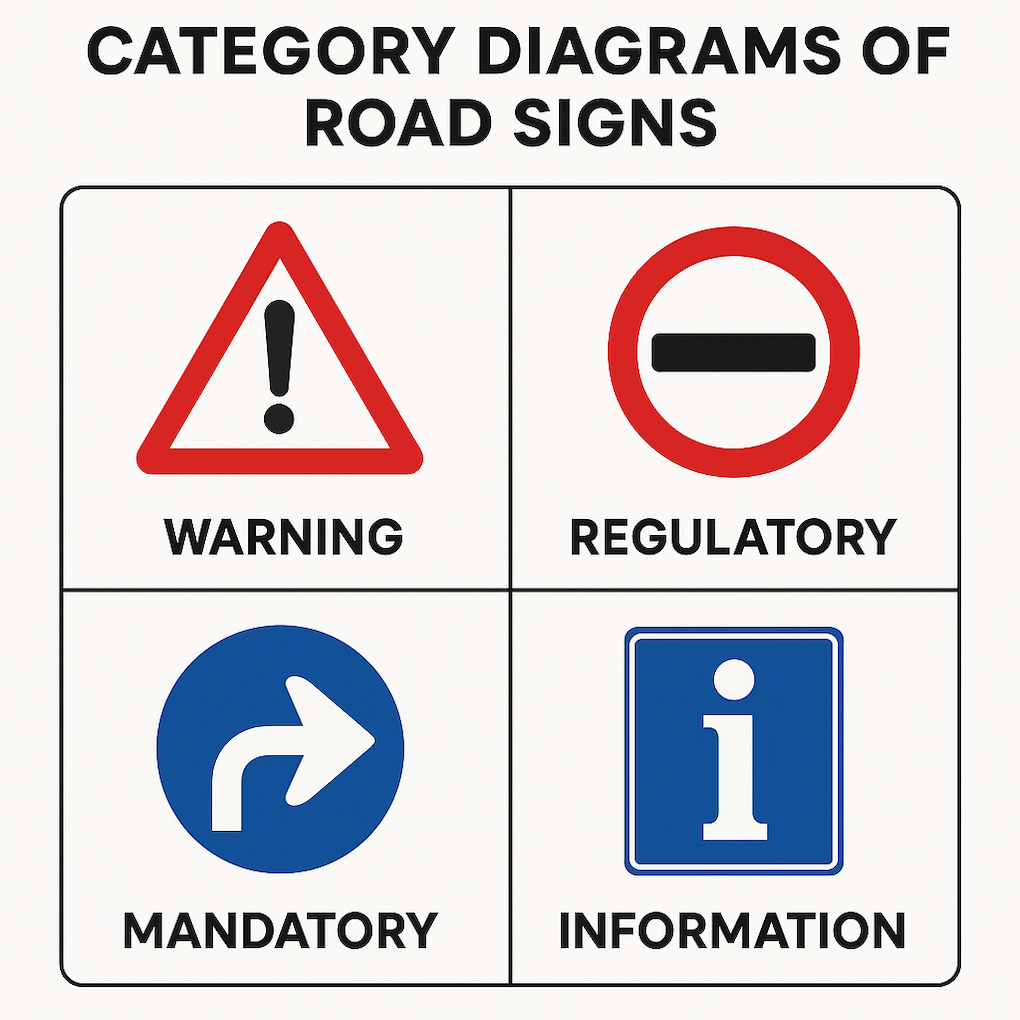
Category Diagrams Of Road Signs in Germany
German traffic signs are divided into three main categories: regulatory signs, warning signs, and informational signs. Each type serves a distinct purpose of guiding and informing drivers and pedestrians.
German traffic signs are systematically organized into straightforward categories:
- Warning Signs (Gefahrenzeichen)
- Regulatory Signs (Vorschriftzeichen)
- Mandatory Signs (Gebotszeichen)
- Informational Signs (Hinweiszeichen)
- Supplementary Signs (Zusatzzeichen)
Each category has specific shapes and colors, making it easy for drivers to recognize and react correctly at a glance.
1. Warning Signs (Gefahrenzeichen)
These signs alert drivers to potential hazards ahead. They are usually triangular with a red border and white background. The symbols inside indicate specific dangers:
- Sharp Curves: Depicted by curved arrows, signaling drivers to slow down.
- Pedestrian Crossings: A figure walking across a road prompts drivers to be cautious.
- Animal Crossings: Deer or wild animal symbols warn of areas where wildlife may cross unexpectedly.
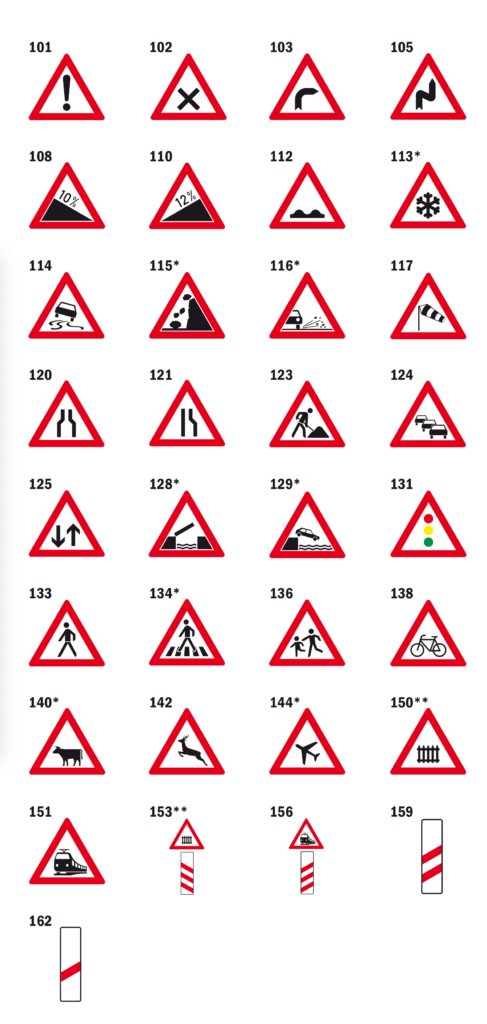

Click here to expand the Warning Signs list
- 101 – Danger ahead (general warning)
- 102 – Intersection with priority to the right
- 103 – Sharp curve to the right
- 105 – Double curves (first right, then left)
- 108 – Steep hill downward (10%)
- 110 – Steep hill upward (12%)
- 112 – Uneven road surface (bumpy road)
- 113 – Slippery road (due to snow/ice)
- 114 – Slippery road
- 115 – Falling rocks (from the right side)
- 116 – Loose gravel (road works)
- 117 – Crosswind (strong winds)
- 120 – Two-way traffic ahead
- 121 – Traffic congestion (possible queues)
- 123 – Road work ahead
- 124 – Traffic lights ahead
- 125 – Two-way traffic crossing
- 128 – Opening or swing bridge ahead
- 129 – Riverbank or quay (danger of driving into water)
- 131 – Pedestrian crossing (traffic lights)
- 133 – Pedestrians crossing
- 134 – Zebra crossing (pedestrians)
- 136 – Children crossing (near schools/playgrounds)
- 138 – Cyclists crossing
- 140 – Domestic animals crossing (farm animals)
- 142 – Wild animals crossing (deer)
- 144 – Aircraft flying low (airport nearby)
- 150 – Railway crossing ahead (with barriers)
- 151 – Tram crossing ahead
- 153 – Railway crossing ahead (without barriers, warning of proximity)
- 156 – Railway crossing ahead (with barriers, warning of proximity)
- 159 – Marker (countdown for railway crossing: 80 meters ahead)
- 162 – Marker (countdown for railway crossing: 240 meters ahead)
The triangular shape and red border universally signify caution. According to the ADAC (Germany’s largest automobile club), ignoring these signs can significantly increase accident risks.
2. Regulatory Road Signs Of Germany

Regulatory signs tell drivers what they must or must not do. These include stop and yield signs, speed limits, prohibitions, and mandatory directions. Stop signs require a complete stop before moving forward. Yield signs mean giving way to other vehicles. Speed limit signs show the maximum speed allowed. Prohibition signs, like “No Entry” or “No Parking”, restrict specific actions. Mandatory signs indicate required actions, such as turning left or right.
Regulatory signs in Germany are primarily circular and come with specific colors and symbols:
- Red circle: Prohibition or restriction.
- Blue circle: Mandatory actions or permitted directions.
- Rectangular or square signs: Provide general information or clarify regulations.
These signs establish legally binding rules; failure to follow them can result in fines or penalties.


209-20 Turn right ahead

209-30 Ahead only

211-20 Turn right

214-20 Ahead or right only

215 Roundabout

224 Bus/tramway stop (also school buses)

222-20 Pass by on right, i.e. keep right

237 Route for pedal cycles only
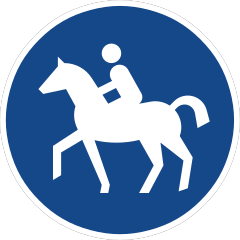
238 Horses only

239 Pedestrians only
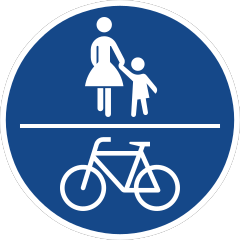
240 Unsegregated route for use by pedal cycles and pedestrians only
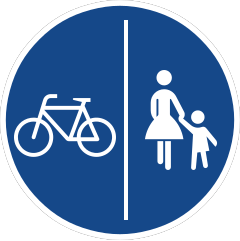
241 Segregated pedal cycle and pedestrian route

245 Buses only
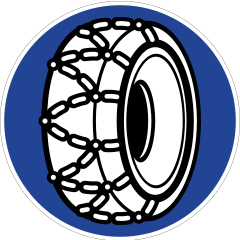
268 Snow chains required

275 Minimum speed

279 End of minimum speed
3. Informational Signs
Informational signs guide drivers and make navigation easier. They include directional signs, parking signs, and motorway signs. Directional signs show routes and distances to towns or landmarks. Parking signs indicate where to park and any restrictions. Motorway signs provide details about exits, rest areas, and speed suggestions.

Priority at next intersection

Priority road

End of priority road

Traffic has priority over oncoming vehicles

Town/city limit sign (front)

Town/city limit sign (back)

Parking area

Parking management zone (entry)

End of parking management zone

Parking on sidewalk allowed

Parking disc

Traffic calming zone

End of traffic calming zone
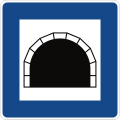
Tunnel ahead

Emergency lay-by

Motorway entrance

End of motorway

Expressway entrance

End of expressway

Motorway exit ahead
Expressway exit ahead

Expressway exit for local destinations ahead

Exit from motorway (arrow sign)

Exit from expressways (arrow sign)
4. Traffic control devices
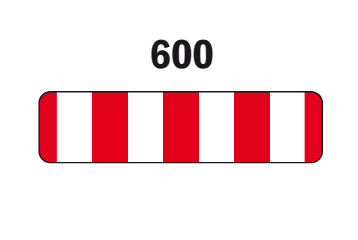
600 Barricade

605 Obstruction marker

610 Traffic cone
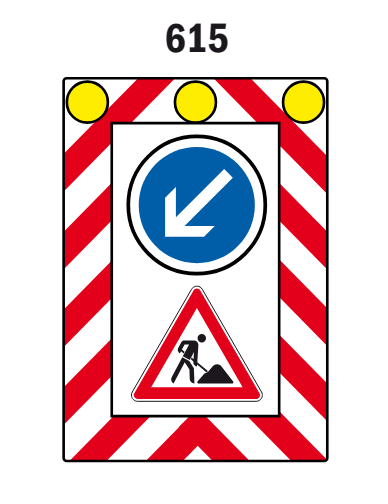
615 Mobile lane closure board
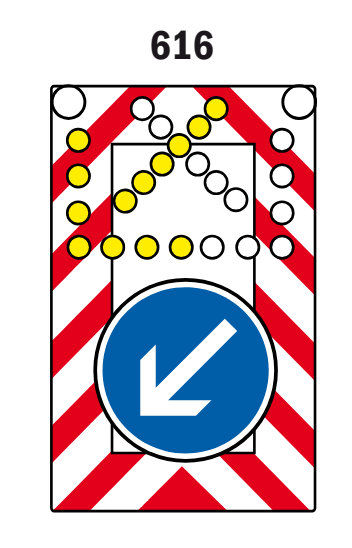
616 Mobile lane closure board with flashing arrow
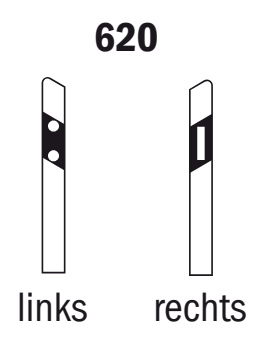
620 Reflector guide posts (left, right)

625 Bend ahead

630 Parking hazard
Traffic signals in Germany are well-structured, following a familiar red, yellow, and green sequence. Yellow lights appear twice—before green and red—to give drivers extra warning time. Pedestrian crossings have their signals marked by red or green figures, ensuring safe passage for walkers. In addition, Germany features unique traffic lights for cyclists and trams, which are separate from standard signals. These additions ensure smoother and safer navigation for all types of road users.
Tips for Understanding Traffic Signs in Germany
If you’re new to revving in Germany, these tips can help:
- Familiarize yourself with the most common signs before driving.
- Use navigation apps that highlight local rules and speed limits.
- Consider attending a driving course if you’re staying short-term.
Understanding traffic signs in Germany is crucial for safe and legal driving. Whether you’re a tourist or a local, prioritizing road safety and compliance with rules will make your experience more enjoyable. Take time to learn and respect these signs—after all, they affect everyone on the road.
FAQ about traffic signs in Germany
1. What do blue traffic signs in Germany mean?
Blue signs indicate mandatory actions, such as specific directions or lane usage.
2. Are German traffic signs different from other European countries?
While similar in many ways, Germany’s signs are their clarity and unique Autobahn-specific signs.
3. What is the penalty for ignoring a stop sign in Germany?
Fines can range from €10 to €70, with potential points on your license.
4. Do German traffic lights have a different sequence?
Yes, yellow appears before red and green lights, offering drivers extra warning time.
5. How can tourists familiarize themselves with German traffic signs?
Using guidebooks, online resources, or navigation apps with local traffic information can help.
How do traffic lights work in Germany?
Traffic lights follow the standard red, yellow, and green system. Yellow comes before red and green to warn drivers when to stop or go.
How many traffic signs are there in Germany?
Germany has over 1,000 official traffic signs, divided into warning, regulatory, and informational categories.
Are stop signs blue in Germany?
No, stop signs in Germany are red octagons with white letters, just like in most countries.
What do road signs look like in Germany?
Road signs use clear symbols and colors: red for warnings or rules, blue for instructions, and white for information.


